

- #Mac command line tool mac os
- #Mac command line tool install
- #Mac command line tool code
- #Mac command line tool download
So the search went on for something simple we could use within a shell script. You need to have the Xcode command-line tools. Since Python 2 is end-of-life, what could be more obvious than switching to Python 3? But we quickly realized that Python is no longer installed by default on macOS. In Python, it’s very simple to get the content of a plist entry. The information offered by the “ Learn More…” button led us to believe that we must be using Python 2 somewhere inside Kaleidoscope.Īnd sure enough, we found it buried in a script to extract the version number of a property list. That’s not the kind of message you want your customers to see less than 3 weeks after releasing a brand new major update.
#Mac command line tool mac os
If you are familiar with installing tools with apt-get, apt, yum or other package manager on Linux, this is the Mac OS equivalent of that.When testing Kaleidoscope 3 on the first release candidate of macOS Monterey, we noticed an alert that we hadn’t seen before: “Kaleidoscope” needs to be updated.
#Mac command line tool install
The Homebrew project allows you to install tools for the command-line from the Terminal itself.
#Mac command line tool code
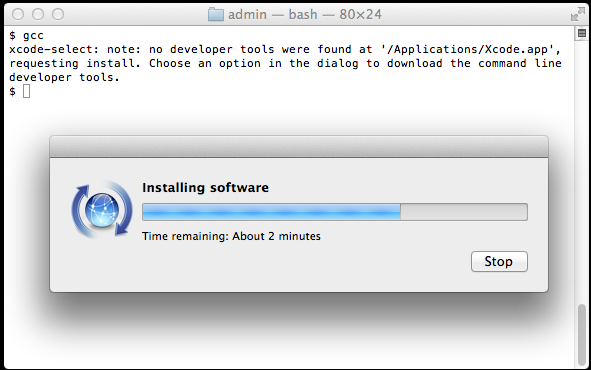
Always test your code on the virtual server before submitting!Īlternative Way to Install Compiler and Tools A small warning is that Clang on Mac will sometimes automatically include certain common header files for you if you forget to include them yourself then your code might compile under Clang on the Mac, but fail to compile on the virtual server's version of Clang in this case you will lose credit in the (Correctness) category for not following the C++ standard. For convenience, the g++ command is also an alias to the clang++ tool, so typing either command will work. The compiler bundled with XCode is the LLVM project's Clang compiler, so you compile with the clang++ command. The following tutorial covers the entire process (it doesn't list Sierra, but it still works for Sierra): You could use the XCode IDE (which is nice, but requires a lot of overhead for small projects), or you could install the command line compilation tools so that you can compile the same way we do in lab and in class.
#Mac command line tool download
If you want to compile locally on OS, you will need to download XCode from the App Store.
Either the source file or the remote file (or even both) may be remote. That is, the remote server's account information is on the left of a single colon, and the path to the file (either relative to your "home" directory or absolute from "/") is on the right. Scp -r homework should see the pattern here: A remote path is always of the form: : path_to_file So, for example, you could copy an entire folder called homework to your home directory on the virtual server with a command like: Scp hello.cpp a second example, the following command would copy a file named hello.cpp from a directory called example that is in your home directory on the virtual server to your local machine in the current working directory (like you would do if you were about to submit hello.cpp to CSCADE):Įssentially the scp command works exactly like the cp command, except that it will work on non-local paths. Where either the source_file or the destination_file (or both) may be located on a remote server! For a concrete example, imagine that you have a file called hello.cpp in your current working directory on your local machine, and that you want to upload it to a directory called example that is in your home directory on the virtual server (again, the last digits in the IP will vary depending on your course and section): You either need a secure file transfer client ( Cyberduck and FileZilla are popular options), or you could use the scp command: If you want to keep a local copy, however, this isn't the easiest strategy. One simple option here is to use Komodo Edit's ability to open/save remote files to edit your programs in-place on the virtual server. To exit the ssh session, just enter the exit command. The server will ask you for your password, and you will be logged in (and placed in your "home" directory). Ssh the xxx is replaced with the last three digits of your virtual server's IP address (see your course website on ). To connect to your class virtual server from the Mac OS Terminal, you just need to use the built-in ssh command:

You can simply drag its icon to your Dock for quick access later. The Terminal app is installed in the Utilities folder beneath the Applications folder (at /Applications/Utilities/Terminal.app). Mac OS already includes a UNIX-based Terminal application that you can use to practice the same UNIX/Linux commands we are using on the class virtual server. As such, most of the functionality you need is either already there or very easy to get. Mac OS is based on BSD-UNIX, with a nice GUI on top.

5 Alternative Way to Install Compiler and Tools.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
